Repository of Water,
the Role of Marshland and Sphagnum Moss
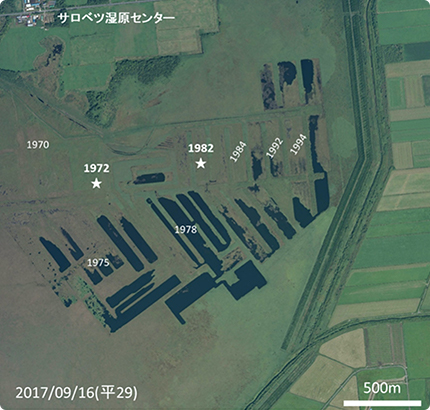
1. Peat mining in Sarobetsu
Marshlands exist in various places in Japan and have a great impact on ecosystems due to their huge water storage capacity. They also have tangible and intangible effects on people’s lives. The importance of marshlands has been reconfirmed since their function has been gradually lost due to excessive development and utilization. They also play an important role as a huge carbon store since peat bogs are formed by plants accumulating without decomposing
Though peat could not be used as energy directly due to its low purity of carbon, it was mined up to a depth of 5 m for the production of peat moss. The volume velocity of peat is approximately 1 cm per year, and a 5 m mining depth is equivalent to 5,000 years of accumulation.
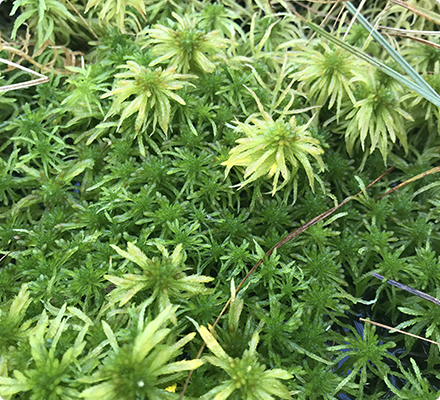
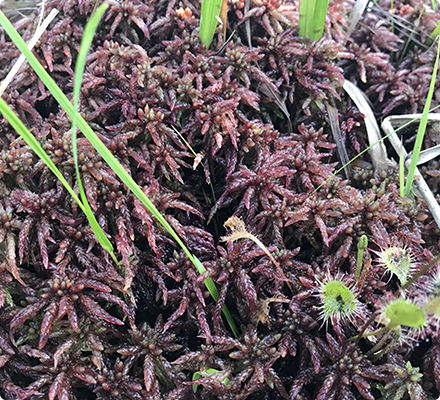
Peat moss, mainly sphagnum moss, is a peat formed by plant accumulation and insolubilization, and is used as a soil conditioner.
2. Efforts toward regeneration
It is essential to form a high moor in the process of peat accumulation. In high moor, sphagnum moss finally grows on the pile of dead plants, and rare species of plants grow on the sphagnum moss.
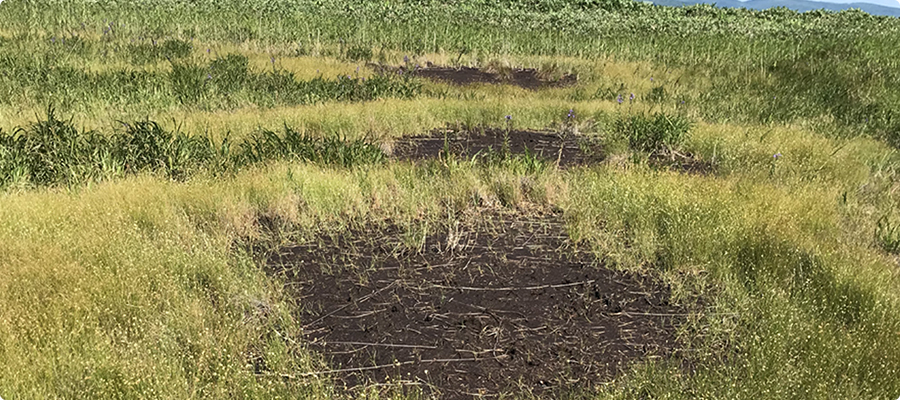
The remaining soil is returned to the peatlands after excavation, and then the floating islands are formed as shown in the above figure. An abnormal transition of plants occurs in which plants grow on those islands. Fig.1 shows a cypress plant that has just invaded the bare land.
A bog-specific plant called Yachibozu gathering and rising (shaved) when some tall plants such as Nomadagaya enter the islands after Mikazukigusa. If drying progresses, reeds and sasa will grow in the soils, and sphagnum moss cannot grow.


3. The role of sphagnum
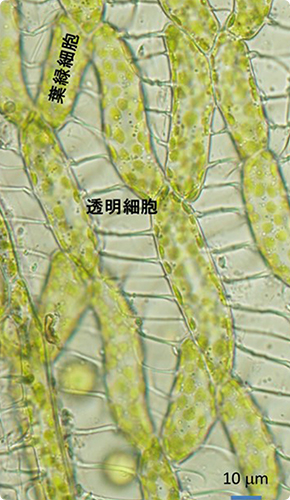
Sphagnum grows naturally above the surrounding water level, to become the climax (polar phase) in the high moor. In addition, it also plays an important role in water storage since it is considered to have the ability to absorb groundwater to a depth of more than 1 m. In the leaves of sphagnum moss, dead cells (so called transparent cells) also exist, in addition to the normal cells necessary for survival. The transparent cells have micro holes and are capable of absorbing and storing water by capillarity.
Sphagnum can grow even in acidic soil, and it is also resistant to drought due to its strong water storage capacity. It is a rare plant that can grow in extreme environments. In the future, various applications can be expected by conducting research targeting biomimetics and living organisms that live in extreme environments.
4. Sphagnum and soil microorganisms
Land changes bare to being colonized by Mizukigusa, Nomagaya, and Sphagnum. However, there are some lands that remain bare. Why can plants not colonize those lands? We have been analyzing soil microorganisms in order to explain this.
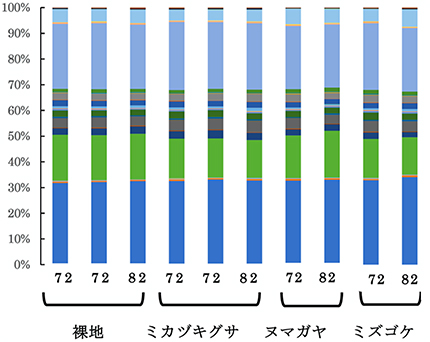
First of all, we have investigated bacterial flora by using 16S applicon analysis. As a result,31 phyla of bacteria were found. We also intend to verify whether the bacterial flora changes depending on the age or transitional state. Furthermore, we plan to verify the fungal structure by using 18S amplicon analysis.
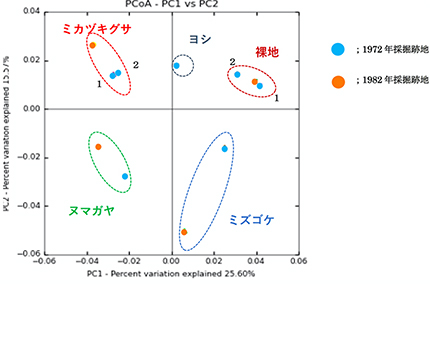
According to the principal coordinate analysis of the bacterial flora structure, the bacterial flora structure of the bare land is very similar to each other, however, the differences are becoming apparent due to the mining ages as it transitions to Cyperaceae, Scutellaria, and Sphagnum.